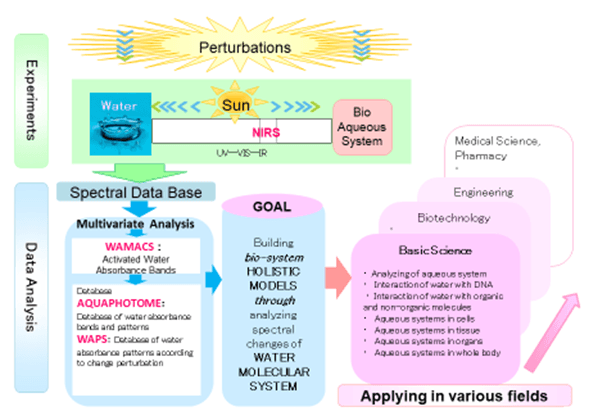
Aquaphotomics: A new science
Aquaphotomics is a new “– omics” discipline introduced by the Laboratory of Bio Measurement Technology at Faculty of Agriculture, Kobe University, Japan. The main object of this new field is to understand the role of the water molecular system by monitoring water spectrum of bio and aqueous systems under various perturbations. Aquaphotomics presents water spectrum as holistic bio marker, which works as molecular mirror, epitomizing the respective system.
Segmented approach for water study
Water is the most widely distributed component of biological systems. Understanding the role of water in such systems is of crucial importance. Water properties have been extensively studied by several research groups. Different methods have been applied to study the chemistry of water itself, from X ray spectrometry to THz spectrometry. However, even if these techniques provide us with valuable information on water systems, they generally focus on water as a physical subject only.
From biology science point of view, up to very recently, biologists have been focusing on pinpointing single biomolecules related to natural phenomena, without considering the contribution of all components of the system, especially water; whereas the function of these molecules are highly related to their structure, which is also highly related to the creation of hydrogen bonds with the surrounding water molecules.
Chemometrics approach
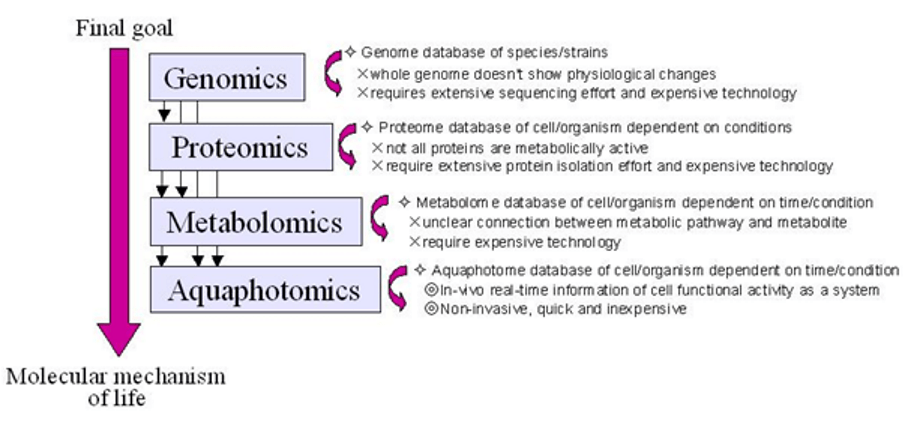
However, in the last decades, life science has taken more systematic approach to revealing the molecular picture of living organisms’ functioning. It is clearly understood that only by combining the previously segmented knowledge and bringing it to a systematic and interconnected database level we can come closer to revealing the intrinsic inter-dependable pathways that represent life.
Both genomics and proteomics have revolutionized life science. Nevertheless creating databases and further using them for metabolic processes research requires isolation of individual elements (genes, proteins) one at a time, making such analyses extremely time consuming and laborious. Moreover it requires destruction of the analyzed object and thus provides a single time-point picture of the processes. Considering the speed, plasticity and multifactor-dependence of metabolic processes it is clear that such static one-at-a-time approach needs to be replaced with more dynamic and real-time methods.
This idea has already been proposed by metabolomics (the science of all metabolites in a cell/organism at a given moment) and is further expanded by the newest omics – aquaphotomics (the science of water interaction with solvents visualized by Vis-NIR light absorbance pattern). Even though these two methods are taking completely different approaches, they try to solve the same problem – to provide systematic, at a glance view of the processes with time-dependent information of their interconnections as well as a speed and possibility to study the same object continually, i.e. to study it non-destructively.
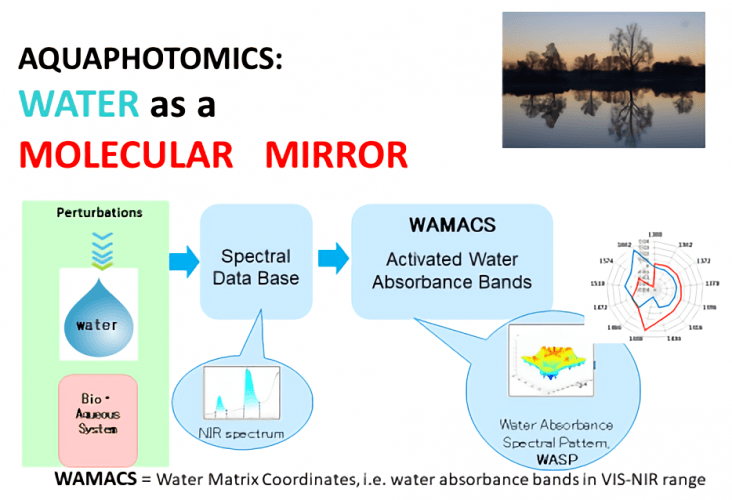
Aquaphotomics: a global, non destructive approach for biological and aqueous systems
Aquaphotomics approach to spectroscopy opens a new area in biological sciences and engineering. It describes a new way for exploring biological systems through a non- destructive monitoring of their interaction with VIS-NIR light. Water emerges as a molecular mirror when VIS-NIR light illuminates the aqua system. Even tiny perturbation to the system as temperature, light, presence of other molecules etc. does change the structure of the water molecular system. These changes are captured and reflected by the water as changes in its spectral pattern. It means that the light that leaves the system and gets back to the surroundings has a different spectrum, i.e. different intensity at each energy level. Spectral analysis reveals that changes with the water matrix under perturbation reflect, like a mirror, the rest of the molecules surrounded by water.
Data processing
The improvement of detectors and moreover the development of supercomputer allows now to acquire immense number of spectra of various systems in real time as time series and under various possible perturbations. However, this huge quantity of data made available confront researchers with new challenges. To appreciate and fully explore the richness of such copious spectral information, new methods yet have to be developed to unravel it, as very often, physical and chemical information are overlapped in the spectrum. Once again, the new supercomputers allow now to process huge amount of information and make them match the computer simulation and modeling.
Methods are yet to be further developed, and water spectra under different perturbations to be systematic acquired, but Aquaphotomics already open new horizons in understanding unknown phenomena in various fields. Once a large database of characteristic waterbands –the aquaphotome- has been acquired, they will be related to specific biological functions, structures… and used for understanding biology, chemistry and physics.
Some important results have already been achieved in life sciences and medicine.
Aquaphotomics vocabulary
Water Matrix Coordinates (WAMACS): Water matrix is defined by the absorbencies of all water species of a sample in a 3D space. Multivariate analysis of such water matrix of a number of similar samples under various perturbations could provide extended knowledge (aquaphotome) about the respective biological sample. The term “WAter MAtrix CoordinateS” (WAMACS) is introduced to capture and present the information about the influence of different perturbations on the water absorbance in VIS-NIR range for various biological samples.
Water Absorbance Pattern (WAP): As water is very easily influenced by various factors, it has been proposed to use the spectral changes of studied aqueous and biological systems, under various perturbations, to learn more about the water matrix and the rest of molecules that are surrounded by water through the changes of water absorbance patterns, WAP, when following respective perturbation.
Aquaphotome: the entire complement of water molecules and light interactions in the presence of other bio molecules, i.e. comprehensive spectral assignment of all existing water absorbance bands. The water absorbance bands of respective systems (WAMACS) found under various perturbations will define the respective aquaphotome for each particular system.
Extended Water Mirror Approach (EWMA): It is assumed that the rest of the elements in a complex system are “reflected” on molecular level by the water. Its composition and structure, described by WAMACS give information for the rest of the elements in the system, as well as, for the water in the same manner as the reflection of a water mirror gives all the visible details of the surroundings.